
Understanding Breast Asymmetry and Its Impact on Women in the US
Breast asymmetry is a common issue many women face in the United States. It’s an imbalance of size, shape, or position between the two breasts and can cause physical discomfort as well as emotional distress. This condition affects thousands of women of all ages, races, and body types, making it important to understand its symptoms, diagnosis options, and treatments available.
Table of Contents:
- What is Breast Asymmetry?
- Definition of Breast Asymmetry
- Causes of Breast Asymmetry
- Types of Breast Asymmetry
- Symptoms of Breast Asymmetry
- Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Breast Asymmetry
- Prevalence of Breast Asymmetry in the United States
- Statistics on the Prevalence of Breast Asymmetry in the US
- Risk Factors Associated with Developing Breasts Asymmetries
- Coping with and Overcoming the Challenges Posed by Breasts Asymmetries
- FAQs in Relation to Breast Asymmetry
- Should I worry about asymmetry in my breast?
- How serious is asymmetry on a mammogram?
- What does asymmetry of the breast indicate?
- Conclusion
What is Breast Asymmetry?
Breast asymmetry is a condition in which one breast is noticeably different from the other. The most common type of breast asymmetry is when one breast appears larger than the other. Other types include when one nipple sits higher or lower than the other or if there are differences in skin texture and color between them.
Definition of Breast Asymmetry
Breast asymmetry occurs when noticeable differences between two breasts make them appear uneven. This includes size, shape, position, skin tone, and texture variations. These discrepancies may be minor enough to go unnoticed but can also be quite pronounced depending on the individual’s case.
Causes of Breast Asymmetry
There are many potential causes for this condition, including genetics, hormonal changes during puberty or pregnancy, trauma to the chest area such as surgery or injury, and certain medical conditions like Poland Syndrome, congenital deformities such as tuberous breasts and more recently plastic surgery procedures gone wrong. In some cases, it could simply be due to natural variation among individuals where no specific cause can be identified.
Types of Breast Asymmetry
The most common type is when one breast appears larger than its counterpart, but this isn’t always true. Sometimes both breasts may look similar yet remain unequal due to their positioning relative to each other on either side of your chest wall (elevation difference).
Key Takeaway: Breast asymmetry is a condition where one breast appears noticeably different from the other. It can be caused by genetics, hormonal changes, trauma, medical conditions, and plastic surgery gone wrong. Types of asymmetry include size discrepancy, nipple elevation difference, and skin texture color differences.
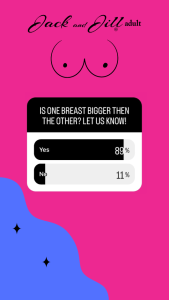
[Breast Asymmetry Poll Infographic]
We ran a poll on our Instagram asking women if they have experienced Brest Asymmetry. 89% of women stated one breast was bigger than the other.
Symptoms of Breast Asymmetry
Physical Discomfort Caused by Breast Asymmetry: Some individuals may experience physical discomfort due to their asymmetrical breasts, such as pain in either breast or backache caused by an imbalance in weight distribution across both sides of the body. In some cases, women may find it difficult to wear certain types of clothing due to their unevenly sized breasts.
Breast asymmetry can be emotionally and physically uncomfortable, but it can be improved with the right diagnosis and treatment options. Next, we will look at how to diagnose and treat breast asymmetry.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Breast Asymmetry
Diagnostic Tests for Identifying Breast Asymmetry: Diagnosing breast asymmetry requires a physical examination and imaging tests such as mammograms, ultrasounds, or MRI scans. During the physical exam, the doctor will measure each breast to determine if there is an imbalance in size or shape. Imaging tests can help identify any underlying conditions causing the asymmetry.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Improving Breast Symmetry: Non-surgical treatments are available to improve symmetry in breasts with mild to moderate asymmetries. These include exercises targeting specific chest muscles and massage techniques designed to reshape the tissue. Other non-surgical options include wearing special bras and inserts that provide additional support and fill out one side of the chest more than the other.
Surgery may be necessary for more severe cases of breast asymmetry to achieve a balanced look between both breasts. The most common surgical procedures are augmentation (to increase size) or reduction (to decrease size). In some cases, a combination of both surgeries may be needed depending on the difference between each side of the chest. Fat grafting can also be used to even out differences in volume between sides by transferring fat from one area of your body into another where it is needed most – such as adding fullness to one side while reducing fullness on another side at once.
Fortunately, there are a variety of diagnoses and treatment options available. By understanding the prevalence of breast asymmetry in the US and associated risk factors, we can better understand how to prevent it from occurring.
“Let’s get symmetrical. Don’t let breast asymmetry hold you back – there are plenty of non-surgical treatments and surgical options available to help you achieve the look you want. #breastsymmetry #beautygoals”Click to Tweet
Prevalence of Breast Asymmetry in the United States
Statistics show that up to 70% of women will have some degree of breast asymmetry, with one breast being larger than the other or having different shapes. This can cause feelings of insecurity and self-consciousness for those affected by it.
Statistics on the Prevalence of Breast Asymmetry in the US
Approximately 30-70% of all women experience some degree of breast asymmetry, with most cases being mild to moderate. In more severe cases, one breast may be significantly larger than the other or have a different shape altogether. Additionally, studies suggest that this condition is more common among younger women and increases as they age due to hormonal changes during puberty and menopause.
Risk Factors Associated with Developing Breasts Asymmetries
Several risk factors are associated with developing breast asymmetries, including genetics, trauma from surgery or injury, hormonal imbalances such as thyroid disorders or polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), pregnancy/breastfeeding history, smoking habits, and weight fluctuations over time. Additionally, certain medications, such as birth control pills, can contribute to this condition by causing an imbalance in hormones, leading to uneven growth between both breasts.
Breast asymmetry is a common issue for many women in the United States and can be emotionally challenging. Fortunately, strategies are available to help individuals cope with the impact and enhance their self-confidence. This section will explore how to deal with and overcome these challenges.
Coping with and Overcoming the Challenges Posed by Breasts Asymmetries
Strategies for Dealing with the Emotional Impact of Breasts Asymmetries: It’s normal to feel embarrassed or insecure about having uneven breasts, but it’s important to remember that you are not alone in this experience. Finding ways to cope with these emotions can help you move forward without feeling ashamed or inadequate. Talking to a therapist or counselor may be beneficial if you struggle emotionally. Additionally, seeking out support groups online or in person may provide an outlet for sharing experiences and advice on coping with any emotional distress caused by your condition.
Achieving body acceptance despite any physical differences can be difficult, but several strategies may help boost confidence levels related to breast asymmetry. These include wearing clothes that fit properly and accentuate both breasts equally; focusing on positive attributes like strength and resilience; engaging in activities that make you feel good; avoiding comparison between yourself and others; practicing self-care rituals like yoga or meditation; setting realistic goals based on what makes you happy rather than what society deems attractive; embracing imperfections as part of who we are instead of trying to hide them away.
Numerous resources are available for those looking for information about coping with their condition, including websites dedicated specifically to providing support regarding issues related to breast asymmetry, such as Evenly. Evenly offers products, educational materials, and a wonderful Facebook group for tips on managing daily life while living with this condition.
Key Takeaway: Key takeaway: Coping with breast asymmetry can be challenging, but it is possible to achieve body acceptance and boost confidence levels by engaging in activities that make you feel good, setting realistic goals, embracing imperfections, and seeking out support.
FAQs in Relation to Breast Asymmetry
Should I worry about asymmetry in my breast?
No, asymmetry in breasts is normal and common. Everyone’s body is unique and slight differences between the two sides of your chest are nothing to worry about. Most people have some degree of asymmetry in their breasts that can be caused by factors such as hormones, genetics, or even lifestyle choices like exercise or weight gain/loss. If you’re concerned about the appearance of your breasts, talk to your doctor for more information on what might be causing it and how you can address any issues.
How serious is asymmetry on a mammogram?
Asymmetry on a mammogram can indicate breast cancer, and it should always be taken seriously. It is important to follow up with your doctor if you notice any asymmetry or other changes in the appearance of your breasts. Your doctor may recommend further tests, such as an ultrasound or biopsy, to determine the cause of the asymmetry. Early detection and treatment are key for successful outcomes, so taking any signs of potential breast cancer seriously is important.
What does asymmetry of the breast indicate?
Asymmetry of the breasts can indicate a variety of underlying issues. It is important to note that some degree of asymmetry is normal and expected in most women. Still, if one breast appears significantly larger or smaller than the other, it may indicate an underlying medical condition such as a tumor or hormonal imbalance. In addition, asymmetrical breasts can also be caused by changes in weight, breastfeeding or aging. If you are concerned about your breast symmetry, you should speak with your doctor for further evaluation and treatment options.
